You have seen that there are a lot of layers in the data folder. What do they represent? Where did the data come from? When and how was the data collected? How precise and accurate is the data? You should be able to find the answers to these by looking at the metadata for the layer.
Metadata is almost universally defined as “data about data” (seeWiki.GIS.com The GIS Encyclopedia). It is a critical and, unfortunately, commonly neglected component of a GIS database. Standards for metadata exist, but typically not all GIS data map layers are documented with the detail specified in the standards.
In QGIS to see the metadata for a layer, right click on the layer in the Layer panel and select Properties… and look at the Information tab.
Activity: Look at the Metadata for a Vector Layer.
Open a new project. In the Browser panel locate the shapefiles folder and the airports shapefile. Add it onto the map. The “Select Transformation” window may appear, simply click OK.
Right click on the airports layer and click Properties.
Examine the metadata for the airports layer by going to the Information panel. Under General, the metadata includes information about the layer name, the data location (Path), and associated files required for shapefiles to work (Sidecar files).
Under Information from provider, Geometry shows the data type. The north, south, east, and west boundaries of the layer (expressed in terms of the georeferencing system) are also given under Extent. Feature count (number of points/lines/polygons in the data set) is also shown.
Under Coordinate Reference System (CRS), the metadata shows that the airports layer uses the Alaska Albers projection under Name, and is measured in feet as shown under Units.The Method shows that this is an Albers Equal Area projection, and we will cover different types of projections in a later class.
Activity: Look at the Metadata for a Raster Layer
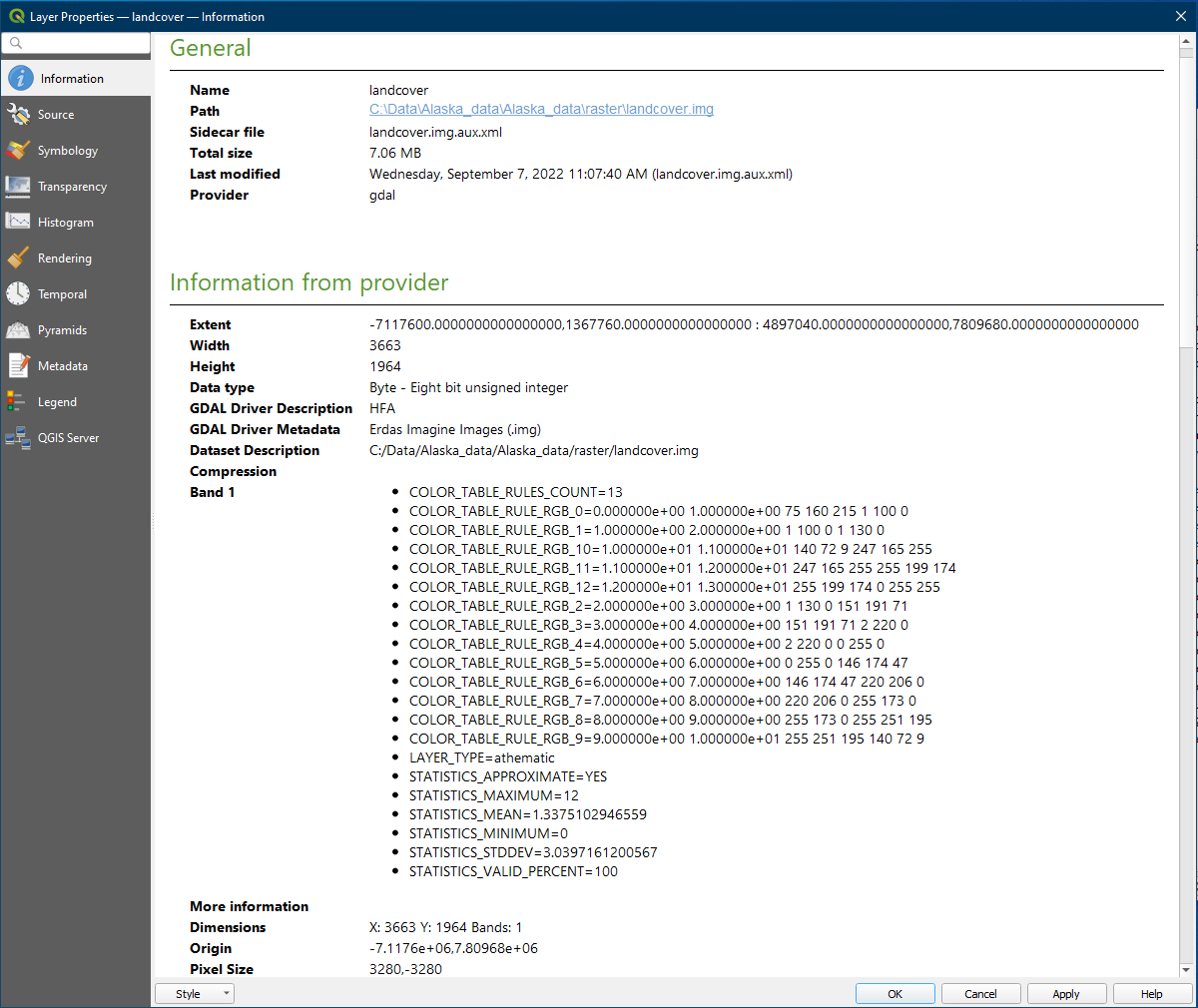
In the Browser panel locate landcover.img within the raster folder and drag it onto the map. Now go to the layer properties by right clicking on the landcover layer and clicking Properties.
Go to the Information section. It contain the data location, projection information, and extent information like vector data. A raster file is made up of columns and rows of pixels. The Width and Height specifies how many columns and rows of cells there are in the layer, and the Pixel Size specifies how large each pixel is, measured using the unit used in the layer, which in this case is in feet (Unit).